In recent years, the future of regenerative medicine has rapidly taken shape, offering hope for millions of people suffering from chronic conditions, injuries, and degenerative diseases. At the heart of this revolution is stem cell therapy, a breakthrough in medical science that is changing how we approach healing and recovery. Rather than relying on invasive surgeries or long-term medication use, regenerative medicine aims to repair and regenerate tissues—unlocking the body’s own healing power.
What Is Regenerative Medicine?
Regenerative medicine is a multidisciplinary field that focuses on rebuilding, replacing, or regenerating human cells, tissues, or organs to restore normal function. It’s a promising alternative to conventional therapies, especially in conditions where damage is considered irreversible.
One of the most exciting tools in this field is stem cell therapy, which uses cells capable of transforming into specialized cell types. This unique ability allows stem cells to repair damaged tissues—whether in joints, muscles, or even internal organs.

How Do Stem Cells Work in Healing?
Stem cells are often described as the body’s raw materials. Under the right conditions, they can divide to form new cells and develop into any number of specialized cell types. In stem cell therapy, these cells are injected into damaged areas of the body, where they begin working to:
- Reduce inflammation.
- Stimulate tissue growth.
- Replace damaged or dead cells.
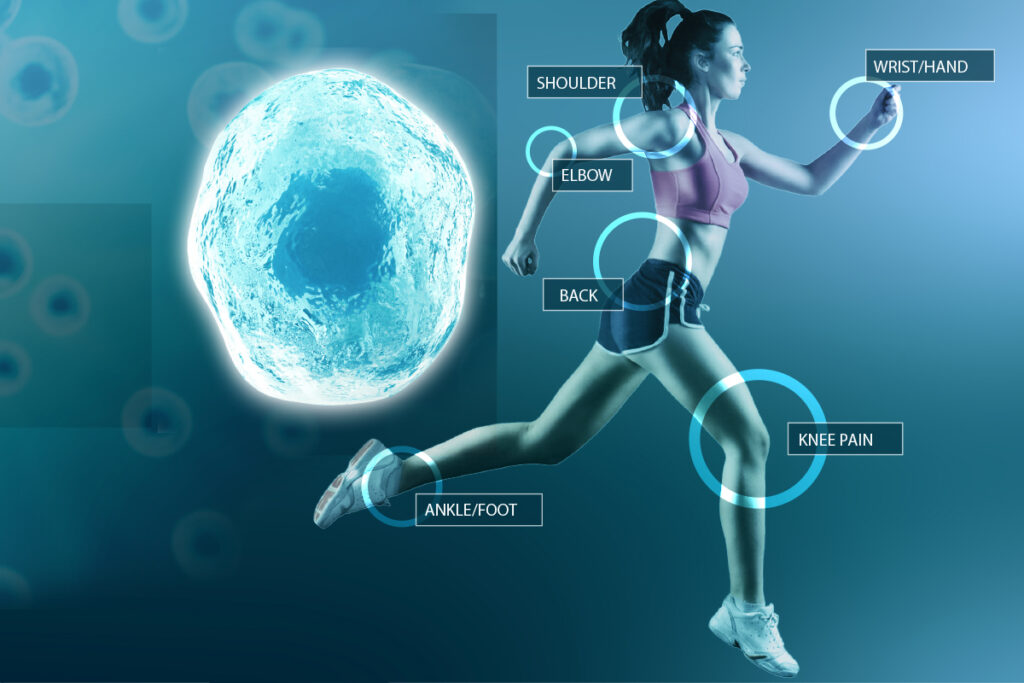
For example, in cases of arthritis or joint injuries, stem cells can encourage the regeneration of cartilage, providing long-term relief and improved joint function. In sports medicine, stem cell therapy is already being used to treat tendon and ligament injuries—reducing downtime and accelerating recovery.
Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy in Modern Healthcare
The future of regenerative medicine is centered around personalized, low-risk, and highly effective treatments. Here are some of the most notable benefits of stem cell therapy:
- ✅ Natural Pain Reduction: Unlike medications that only mask the pain, stem cell therapy targets the root cause—helping reduce pain by healing the actual damage.
- ✅ Faster Recovery Times: Patients report quicker returns to daily activities compared to surgery or long-term therapy.
- ✅ Minimally Invasive: Most treatments involve simple injections, not extensive operations.
- ✅ Low Risk of Rejection: When using stem cells derived from the patient’s own body, the chances of immune rejection are minimal.
Breakthroughs in Stem Cell Research
The applications of regenerative medicine are expanding rapidly thanks to ongoing research. Scientists are now exploring stem cell therapy for:
- Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s and multiple sclerosis.
- Autoimmune diseases like lupus and Crohn’s.
- Heart disease and cardiovascular damage.
- Type 1 diabetes and chronic kidney conditions.
As clinical trials advance, we’re likely to see even more innovative therapies emerge, offering solutions that were once thought impossible.
Is Stem Cell Therapy Right for You?
If you are dealing with chronic pain, joint degeneration, or a non-healing injury, you may be a candidate for stem cell therapy. At San Miguel Health, we specialize in regenerative treatments designed to restore mobility, reduce discomfort, and improve your overall well-being.
Every patient receives a personalized evaluation to determine the most effective treatment plan. Whether you’re an athlete recovering from injury or someone dealing with age-related joint deterioration, our stem cell therapy programs are designed to help you get back to doing what you love.
Take the Next Step Toward Healing
The future of regenerative medicine is here, and you can be part of it. Don’t settle for temporary relief when long-term healing is possible. At San Miguel Health, our expert team is ready to guide you through your options and help you experience the benefits of advanced regenerative care.
Explore our services or schedule a consultation to learn more about how stem cell therapy can transform your health.