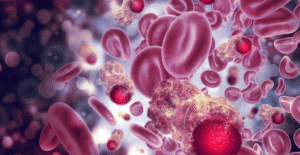
Regenerative medicine has revolutionized healthcare, offering innovative solutions for treating various conditions. While stem cell therapy is widely known for its role in sports injuries and joint pain, its potential in managing chronic diseases is gaining significant attention. From autoimmune disorders to degenerative conditions, stem cells provide new hope for patients seeking alternative treatments beyond traditional medicine.

How Stem Cell Therapy Works in Chronic Diseases
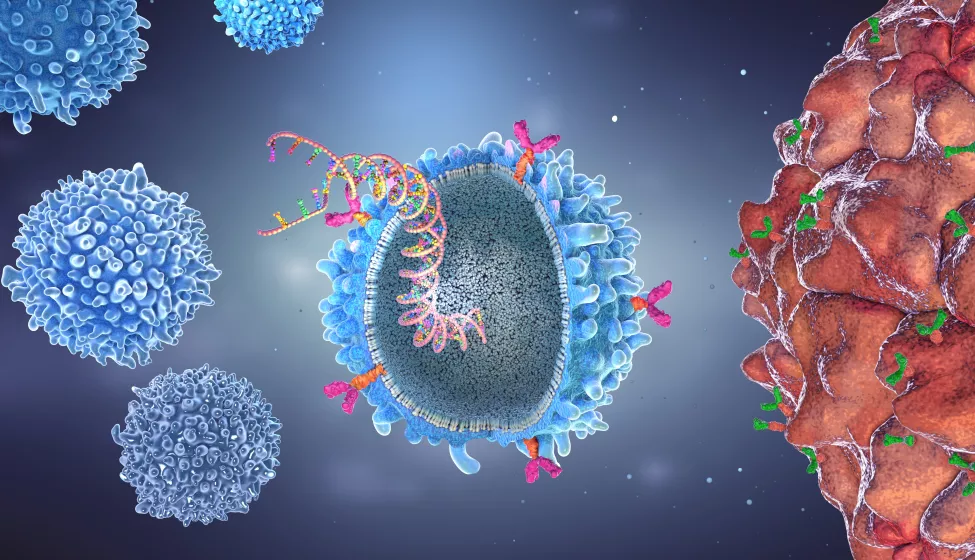
Stem cell therapy utilizes the body’s natural ability to repair damaged tissues. By introducing stem cells into affected areas, these regenerative treatments can reduce inflammation, promote cell regeneration, and restore function. The key benefits of stem cell therapy in chronic disease management include:
- Reducing Inflammation – Stem cells help modulate the immune response, which is crucial for autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis.
- Regenerating Damaged Tissue – In conditions like Parkinson’s disease or heart disease, stem cells support the repair and replacement of deteriorated cells.
- Enhancing Healing and Pain Relief – Patients with conditions such as osteoarthritis experience improved mobility and reduced pain through targeted stem cell treatments.
Chronic Diseases That Benefit from Regenerative Medicine
Research continues to uncover how stem cells can be applied in treating chronic conditions. Some of the most promising areas include:
- Arthritis and Joint Disorders – Stem cell therapy for arthritis is a non-surgical alternative to joint replacement, helping to regenerate cartilage and reduce pain.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases – Studies suggest that stem cells may slow progression in conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease by supporting neuron repair.
- Diabetes Treatment – Regenerative medicine advancements focus on using stem cells to regenerate insulin-producing beta cells, offering potential relief for type 1 diabetes.
- Cardiovascular Disease – Stem cells show promise in repairing damaged heart tissue and improving function after heart attacks.
The Future of Regenerative Medicine in Chronic Care
The field of regenerative medicine is rapidly evolving, with breakthroughs in stem cell research expanding its applications. Scientists continue to explore new ways to harness stem cells for treating previously untreatable conditions. As clinical trials progress, patients may soon have access to even more effective and personalized treatments.
Conclusion
For individuals battling chronic diseases, regenerative medicine offers a new frontier of possibilities. With ongoing advancements, stem cell therapy is proving to be a game-changer in the way we approach long-term health management.
Explore our services or contact us to learn more about how regenerative treatments can benefit you.